A refrigerator is an electric device that uses a closed-loop system to vent heat out of the device and keep the food fresh. It utilizes the refrigerant which flows in coils throughout the device. So, how does a refrigerator work?
Read the full article to get detailed knowledge about it.

What is Refrigerant?
Refrigerant is a cooling agent that absorbs heat and leaves cool air behind to cool the refrigerator, air conditioners, freezers, and vehicle air conditioners. It is a thermodynamic process that repeats continuously to convert the refrigerant from a liquid into a gas and back again. Refrigerants have low evaporation points that do not evaporate easily into the air.
Typically, chlorofluorocarbons were used as refrigerants. As these agents have an ozone-depleting effect, they tend to be less eco-friendly and are not used these days. The most commonly used refrigerants nowadays are R-134a and R-438a.
Refrigerator’s Main Components
Compressor
The compressor acts like the heart of the refrigeration mechanism. In the refrigeration cycle, the evaporator converts the refrigerant in liquid form into low-pressure gas.
When the compressor receives the low-pressure gas from the evaporator, it compresses the gas and increases its pressure and temperature. It circulates the refrigerant throughout the refrigeration system. The high-pressure and high-temperature gas is then pumped into the condenser.
Condenser
The condenser is a cooling device. It is on the back side of the refrigerator. When it receives the hot refrigerant gas, it removes its heat. Thus, it cools down the high-pressure gas and condenses it into a liquid.
Expansion Valve
When the newly converted liquid refrigerant moves inside the expansion valve, it drops the temperature and pressure of the liquid refrigerant to allow its expansion. The expansion valve is a capillary tube in which the liquid refrigerant is routed and sprayed into the low-pressure environment of the evaporator.
Evaporator
The evaporator is located inside the refrigerator and is the refrigeration system’s cooling component. It absorbs heat from inside the refrigerator. Inside the evaporator, the evaporation process occurs, which converts the liquid refrigerant into a gas. This process cools the area around it and generates a proper cooling environment to store foods.
Thermostat
The thermostat monitors the temperature and controls the cooling process. When the temperature inside the refrigerator decreases to a certain limit, it turns off the compressor. When it senses high temperature, it turns on the compressor and begins the refrigeration cycle.
How Does a Refrigerator Work? A Step-by-Step Guide
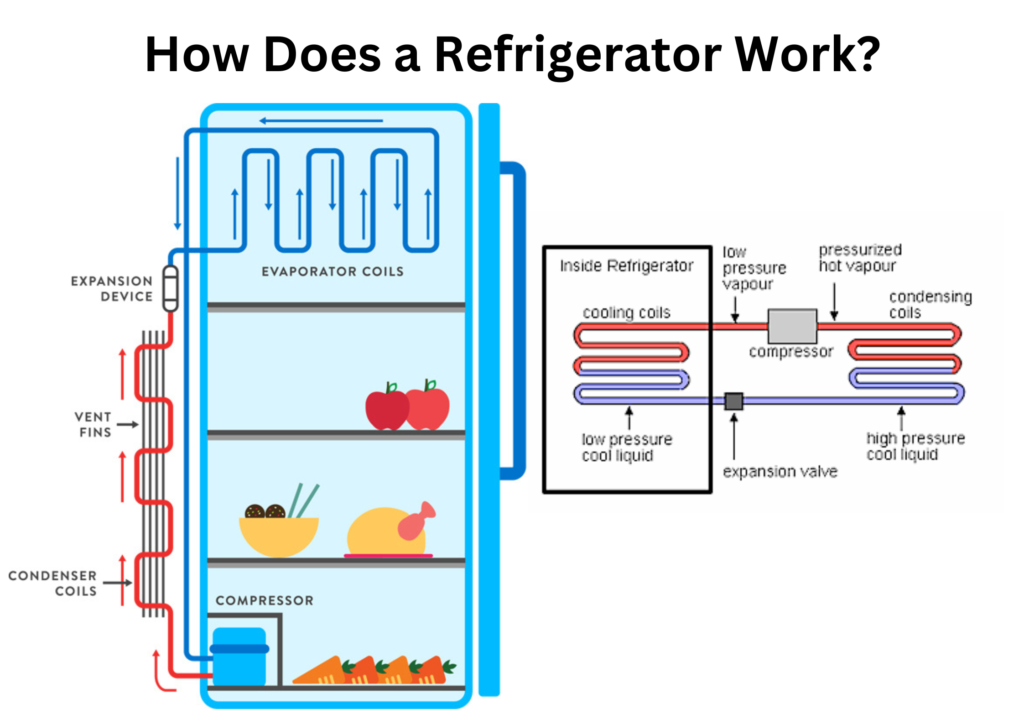
Step 1: Refrigerant compressed
The compressor draws in the refrigerant vapor, compresses it, and increases its temperature and pressure. Then it pushes the high-temperature and high-pressure gas through the condenser coils.
Step 2: Refrigerant converts from gas to liquid
The condenser coils are positioned outside the refrigerator. When the hot pressurized refrigerant moves through the condenser coil, the cooler air in the outside environment exchanges the heat and converts it into liquid form.
Step 3: Refrigerant’s pressure decreases
The cooled liquid refrigerant then passes through the expansion valve before entering into the evaporator. Inside the expansion valve, the refrigerant’s pressure is decreased to allow its expansion. The expansion valve is a capillary tube in which the liquid refrigerant is routed and sprayed into the low-pressure environment of the evaporator.
Step 4: Refrigerant converts from liquid to gas
When the refrigerant moves out of the expansion valve and reaches the low-pressure open space, the liquid refrigerant converts into gas. The evaporator coil absorbs and releases the heat from the refrigerant throughout the process.
Step 5: Refrigerant keeps the refrigerator compartment chilled
The refrigerant absorbs the heat inside the refrigerator, cools the air, and keeps the refrigerator compartment chilled. The chilled air inside the refrigerator helps to keep the food fresh.
Step 6: Vaporized refrigerant flows back into the compressor
The refrigerant evaporates into a gas and flows back into the compressor. The vaporized refrigerant again converts into liquid and the process continues to keep the refrigerator cool.
The refrigerator is a closed system where the refrigerant compression and expansion continue to maintain the temperature inside the refrigerator at a desired level.
How Many Watts Does a Refrigerator Use?
A refrigerator is one of the biggest household appliances in a home. As it remains powered on all day and night, you must be curious to know “How many watts does a refrigerator use?”.
And the simple answer is a refrigerator uses approximately 360W to 720W of electricity.
The power consumption of an electrical device is calculated by using a formula
P = V * I
Here P = Electric Power in Watt
V = Potential difference or, voltage in Volts
I = Current in Ampere
A general refrigerator uses approximately 3A to 6A current and 120V of voltage.
Again, a compressor runs only 30% of the time, so divide the total wattage by 3 to know the average running wattage per day.
If a refrigerator uses 6A current and 120V of voltage, then the power consumed by the refrigerator is
P= 6 x 120 = 720 Watts
As the compressor runs 30% of the time, Power consumption per day is
720W / 3 = 240 watts per day
240W x 24 hours = 5760W
5760W/ 1000 = 5.76 Kilowatt hours
5.76 kWh x 0.10per kWh = $0.576 per day
The monthly electricity bill can be calculated as
$0.576 x 30 = $17.28
The power or wattage used by a regular refrigerator is based on several factors such as its age, size, type, etc. An older model refrigerator consumes more power than a newer model. A large size of refrigerator uses more electricity than a small or mini refrigerator. Again, a top-mount fridge consumes less electricity than a refrigerator with side-by-side counterparts.
While purchasing always prefer an energy-stared certified refrigerator which is 9% more efficient than regular refrigerators.
How Many Amps Does a Refrigerator Use?
The amount of electric current used by the compressor to cool the refrigerator’s compartment is denoted as the refrigerator’s amps. A regular household refrigerator uses an average 3A to 5A current to operate. Whereas, a commercial refrigerator uses up to 20A current for its operation. A mini refrigerator uses under 1A to 2A electric current. The electric current used by a refrigerator depends on the model, size, and type of the refrigerator.
Follow the below steps to learn the amps used by a refrigerator.
- How many amps your refrigerator uses is specified in its user manual or on the manufacturer’s website.
- You can also calculate amps in another way i.e.,
Current (Amp) = Electric power (Watt)/ Voltage (Volts)
The power consumption of a refrigerator is defined in its user manual or on the manufacturer’s website. Most refrigerators in the United States operate on 120 Volts. Thus, you can calculate the electric current consumed by the refrigerator.
- You can also use a power meter to measure the electric current consumed by the refrigerator.
How Much Does a Refrigerator Weigh?
A regular household refrigerator weighs between 200 to 300 pounds. The weight of a refrigerator depends on its size, type, and model.
Also Read
- 8 Reasons Why Refrigerator Not Cooling and Solutions
- Side By Side Vs French Door Refrigerator 2024
- Counter Depth Refrigerator vs. Standard Refrigerator: Which One Is Better?
- Where Should I Place My Air Purifier? 2024
- How Do You Know If You Need an Air Purifier? 2024
- HEPA Air Purifier: Definition, Types, Uses, Efficiency, Working Principle
- Whole House Air Purifier: Types, Pros, Cons, Working Principle 2024
- Air Purifier Advantages and Disadvantages
- How Do Air Purifiers Help? 6 Benefits
- Whole House Dehumidifier: Types, Working Principle, Pros, Cons 2024
- How Does a Commercial Dehumidifier Work? 2024
- How Does a Dehumidifier Work? Types, Uses, Benefits 2024
- 10 Tips for Buying a Dehumidifier
- Dehumidifier Vs Air Purifier 2024
- Dehumidifier vs. Air Conditioner 2024
- Cool Mist Humidifier: Types, Uses, Benefits, Working Principle 2024
- Do Humidifiers Help with Air Quality? 2024
- When Do You Need a Humidifier? 8 Common Signs
- How Do Humidifiers Work? A Complete Guide 2024
- How Humidifier Helps Breathing? 2024
- Humidifier Vs Dehumidifier Vs Air Purifier: Which One Should You Buy? 2024


9 thoughts on “How Does a Refrigerator Work? A Step-by-Step Guide 2025”